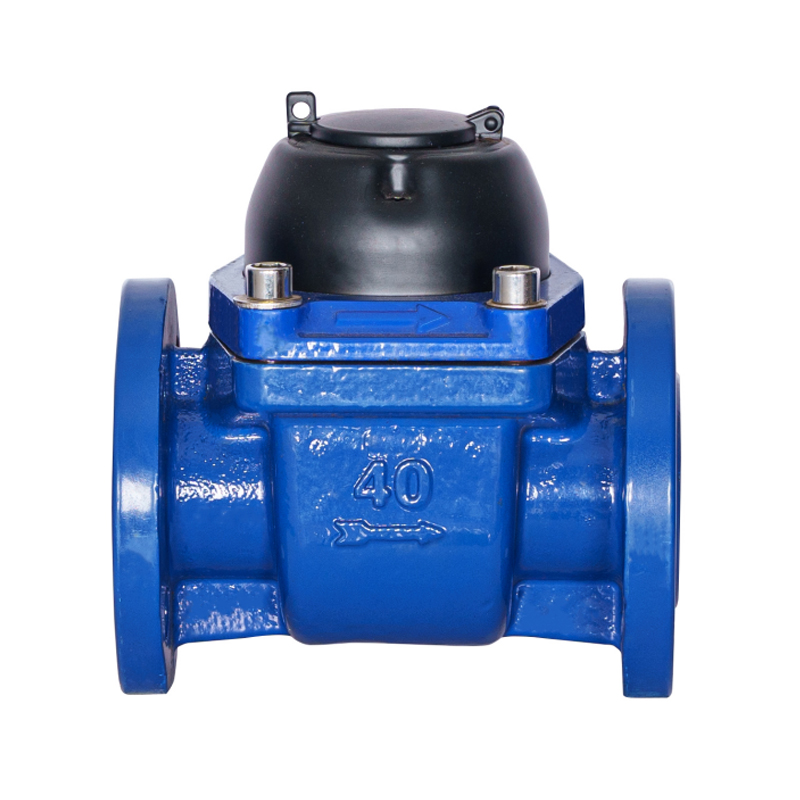
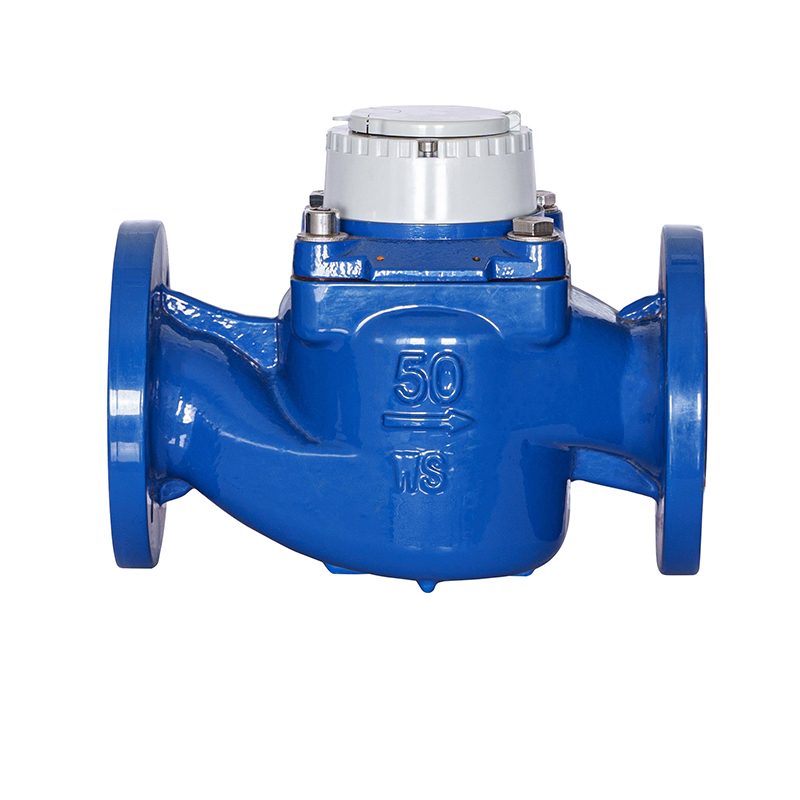
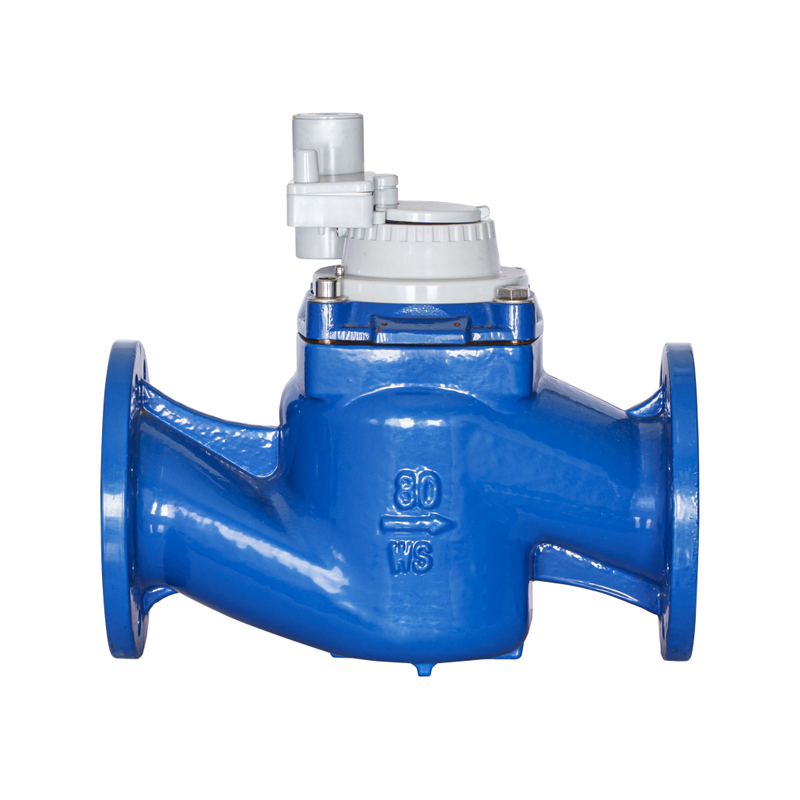
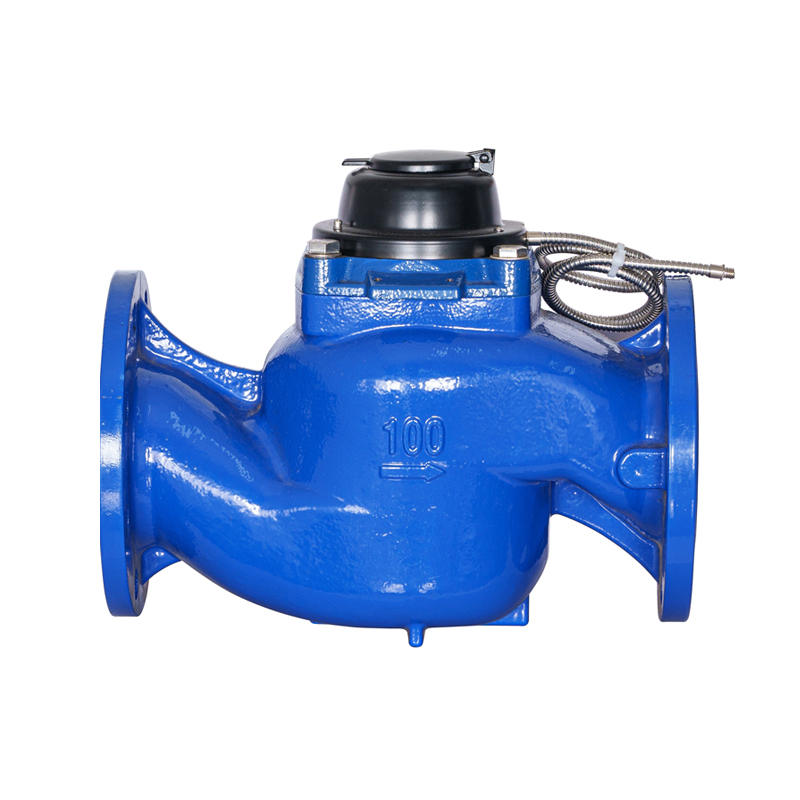
Structural Features of the WS vertical spiral wing water meter Related to Anti-Theft Design
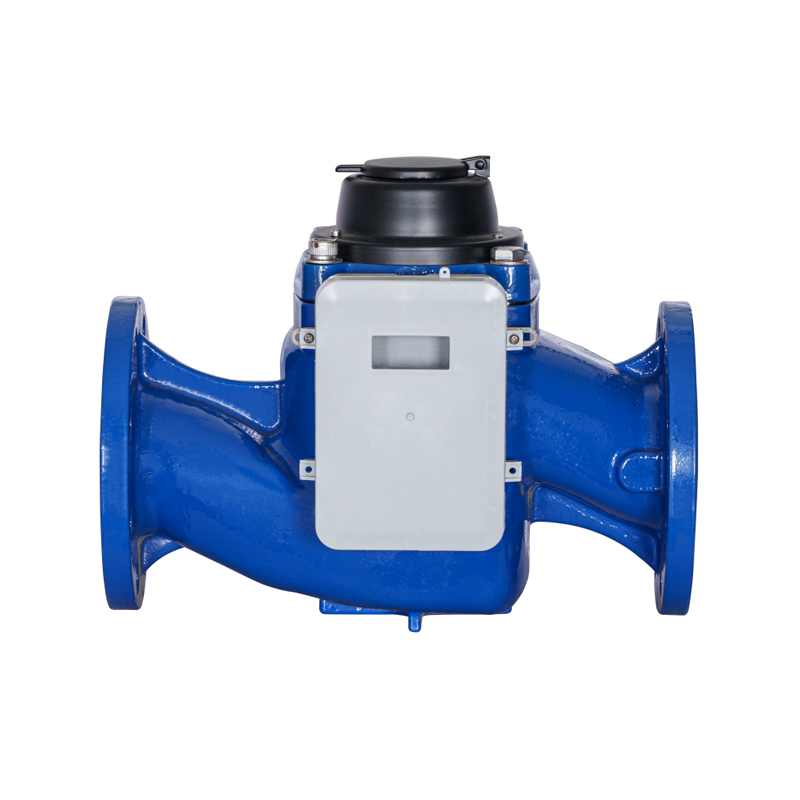
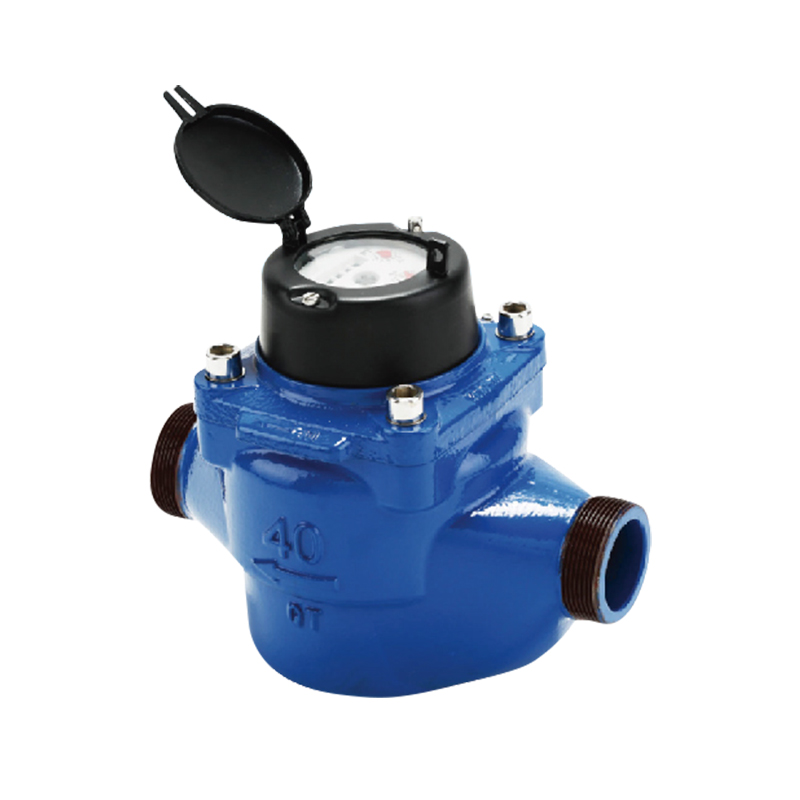
The WS vertical spiral wing water meter is designed with structural considerations that support reliable measurement while offering functional protection in environments where tampering risks may occur. As a type of vertical water meter used in residential, commercial, and agricultural settings, it typically incorporates a configuration where internal components are housed within a sturdy shell to reduce external interference. When anti-theft devices are included, they focus on safeguarding the counting mechanism, inlet and outlet connections, and external covers. The body structure of the WS vertical water meter often allows secure positioning of covers or locking accessories without affecting water flow measurement. The vertical arrangement of the impeller and transmission components provides stability during operation, and this configuration helps align external sealing points that can accommodate lead seal installation. Even though anti-tampering features vary among models and manufacturers, the fundamental structure of a WS vertical spiral wing water meter supports the integration of such mechanisms to maintain reliable performance in the field.
Functional Purpose of Anti-Theft Devices in a vertical water meter System
In water management systems, anti-theft devices play a practical role in maintaining billing accuracy, protecting infrastructure, and preventing unauthorized disassembly. For a vertical water meter used in shared spaces, apartment buildings, or rural supply points, tampering can lead to inconsistencies in consumption records, affecting water providers and users. The anti-theft measures provided on a WS vertical water meter often include locking rings, tamper-evident covers, and concealed fastening points that make it difficult for users to disconnect or alter any part without leaving visible marks. These features contribute to operational integrity by reducing the likelihood of meter bypassing or deliberate manipulation of reading components. When combined with proper installation and monitoring practices, an anti-theft mechanism supports stable system management and helps reduce maintenance demands associated with unauthorized intervention.
Lead Seal Location Design and its Role in the WS vertical spiral wing water meter
A lead seal location is a commonly used feature in water meters to provide tamper evidence. On a WS vertical spiral wing water meter, the lead seal point is often integrated at a junction where the register cover meets the meter body or at positions near the fastening screws and connectors. The design ensures that the seal must be broken before access to internal components is possible, making any tampering attempt visible during inspections. The structural layout of a vertical water meter typically offers specific mounting holes or designated protrusions for securely attaching the lead seal wire. Because the WS vertical water meter uses a vertical impeller arrangement, the upper housing plays a greater role in itemizing seal points, which designers consider when defining the lead seal location. The lead seal provides a simple yet effective way to monitor unauthorized access while maintaining normal usage conditions and ease of reading for users.
Interaction Between Anti-Theft Components and Meter Accuracy in a vertical water meter
Anti-tampering mechanisms in a WS vertical spiral wing water meter must coexist with the meter’s operational accuracy. The measuring unit relies on the rotation of a spiral wing or vertical impeller that responds to water flow. If anti-theft parts obstruct any segment of this movement, or if they introduce pressure on the casing, the reading accuracy could be influenced. Manufacturers generally design anti-theft accessories to stay external to the measurement chamber, ensuring that sealing points, lock rings, or external caps do not compress or distort the meter shell. For a vertical water meter installed in pipelines where pressure fluctuations occur, maintaining the structural balance of both the body and anti-theft features is important. The anti-theft components complement the measurement mechanism rather than interfere with it, preserving the functional reliability expected in environments that rely on precise volumetric readings.
Common Anti-Theft Methods Used in WS vertical spiral wing water meter Installations
Various anti-theft methods are applied during installation of WS vertical water meter units to minimize unauthorized handling. These methods remain externally applied and do not alter the internal hydrodynamic characteristics of the vertical water meter. Techniques may include the use of locking clamps that secure the meter body to the pipeline, sealing wires threaded through purpose-designed holes, and anti-tamper lids fixed over register covers. Some installations add protective boxes around the meter, which incorporate lockable panels or windows that allow reading visibility without exposing the meter body. The goal of these methods is to create a barrier against unauthorized contact while allowing routine maintenance and reading checks. Because the WS vertical spiral wing water meter operates effectively in locations ranging from municipal pipelines to residential systems, these anti-theft methods accommodate diverse installation environments.
Lead Seal Materials and Application Procedures for WS vertical water meter
Lead seals used in a WS vertical spiral wing water meter installation are typically made from materials that deform during crimping but retain clear markings. Although they are commonly termed “lead seals,” modern versions often incorporate aluminum or other softer metals that can accept stamped identifiers. During installation, a sealing wire is threaded through the designated hole or post on the WS vertical water meter body, and the metal seal is crimped using specialized pliers. This crimp captures a unique imprint that indicates the authority responsible for installation or inspection. The seal is placed in a position where it cannot be removed without cutting the wire, providing inspectors with an immediate visual indication of tampering. The placement and accessibility of the seal depend on the meter’s structural design, which in a vertical water meter generally positions sealing points at the top or side to align with the register housing.
Comparative Overview of Anti-Theft Features in Common Water Meter Types
Understanding how the WS vertical spiral wing water meter compares with other water meter types helps clarify how its anti-theft design fits into broader industry practices. While horizontal meters, rotary piston meters, or multi-jet meters also use tamper-evident features, the vertical orientation influences where and how the anti-theft components are applied. The following table illustrates relevant comparative aspects:
| Water Meter Type | Anti-Theft Options | Lead Seal Position | Typical Use Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| WS Vertical Spiral Wing Water Meter | Locking rings, sealing wires, tamper lids | Upper housing or connector area | Municipal and building pipelines |
| Horizontal Multi-Jet Meter | Sealed screws, external lock plates | Side of register cover | Residential zones |
| Rotary Piston Meter | Tamper caps, sealing clamps | Register-to-body junction | Commercial water lines |
| Compound Meter | Multiple sealing points | Separate chambers for high/low flow | Industrial sites |
Role of Installation Standards in Supporting Anti-Theft Performance
Installation standards influence how effectively anti-theft components operate on a WS vertical water meter. Installers typically follow guidelines that specify orientation, distance from valves, and accessibility of meter faces, ensuring that tamper-evident parts remain secure. If the meter is installed with excess strain on connectors or without proper alignment, the designated lead seal point may not align correctly with sealing wires. Many regulatory frameworks require inspectors to confirm that seals are intact after installation. The position of the meter—particularly in underground chambers or exposed wall-mounted structures—affects how easily anti-theft devices can be tampered with. A vertically positioned meter such as the WS vertical spiral wing water meter relies on installers to maintain clear visibility of the sealing points to facilitate routine monitoring.
Material Durability of Anti-Theft Devices Used on vertical water meter Products
Anti-theft components used on a WS vertical water meter are generally selected to withstand environmental conditions such as humidity, sunlight, dust, and temperature fluctuations. Locking rings may incorporate stainless steel or UV-resistant plastics, while sealing rings are chosen for corrosion stability. Since the WS vertical spiral wing water meter may operate outdoors or in semi-exposed meter boxes, the materials must maintain structural strength over extended use. The lead seal wire must resist corrosion to prevent accidental breakage, which could trigger false tamper alerts. Register cover materials also support lead seal placement, requiring sufficient rigidity to hold drilled or molded sealing holes without cracking. By using carefully selected materials, manufacturers strengthen the anti-tampering performance while supporting long-term functionality of the vertical water meter.
Effects of Environmental Conditions on Anti-Theft and Lead Seal Effectiveness
Environmental factors can influence how well anti-theft devices and lead seals perform in real-world conditions. High humidity can cause corrosion on sealing wires, particularly in installations located near coastal regions or underground chambers. Extreme heat might soften plastic components, while prolonged UV exposure could affect tamper lids used on outdoor installations. Since the WS vertical spiral wing water meter functions across a wide range of environments, anti-theft features must withstand these conditions without reducing meter performance. Temperature fluctuations can also affect the fit between meter covers and sealing components, making proper installation important to prevent movement that could weaken the sealing point. By evaluating environmental influences at installation sites, utility personnel can select suitable anti-theft accessory materials to enhance durability.
Integration of Anti-Theft Design with Meter Reading and Maintenance Needs
The anti-theft design of the WS vertical water meter must allow for routine reading and maintenance without compromising security. Many meters incorporate transparent registers or magnifying lenses so that utility staff can read consumption values without removing protective covers. Tamper lids with viewing windows are another option that can align with the vertical design of the WS vertical spiral wing water meter. Maintenance personnel may occasionally need access to connectors or internal parts, requiring seals to be cut during authorized service. After maintenance is complete, new lead seals are applied to restore tamper-evident protection. This process provides a balance between operational needs and security requirements, ensuring the vertical water meter can be serviced while still preventing unauthorized access.
Considerations for Selecting Anti-Theft Accessories for WS vertical spiral wing water meter Installations
When choosing anti-theft accessories for a WS vertical spiral wing water meter, utility providers consider installation location, exposure level, pipeline pressure, and monitoring frequency. For meters placed in public areas, more robust anti-tampering devices—such as lockable meter boxes—may be added. For meters installed inside buildings, simpler sealing measures may suffice. The location of the lead seal point should be easy for inspectors to access and monitor for tampering evidence. The vertical design of this meter type allows flexible placement of seals at the upper or lateral housing areas, depending on the model. Utility providers may also standardize anti-theft accessory types across installations to simplify inspection procedures and inventory management.



 عربى
عربى