Provide Customers With High-Quality Water Meter Products
Custom Industrial Smart Water Meter Manufacturers
-

WPD/DN40-DN200 R200 Wide Range Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
This series of products is a new generation of wide-range horizontal spiral vane water meters developed by the Water Cub... -

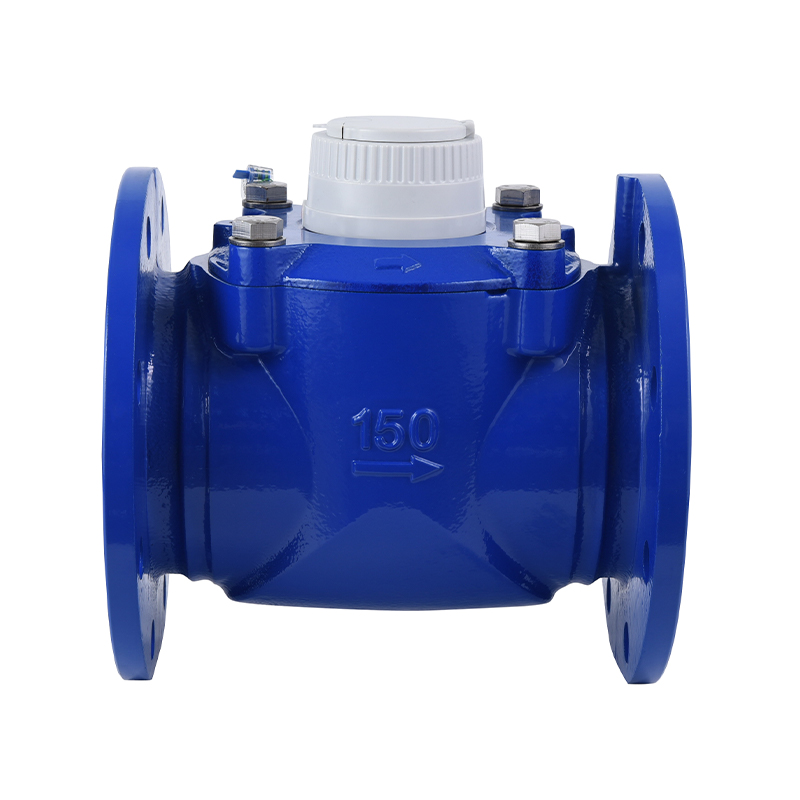
Large Caliber Water Meter Pulse Remote Transmission Sensor Assembly
Stable and reliable long-distance transmission of meter data to AMR/AMI system All types of large-diameter water meters ... -

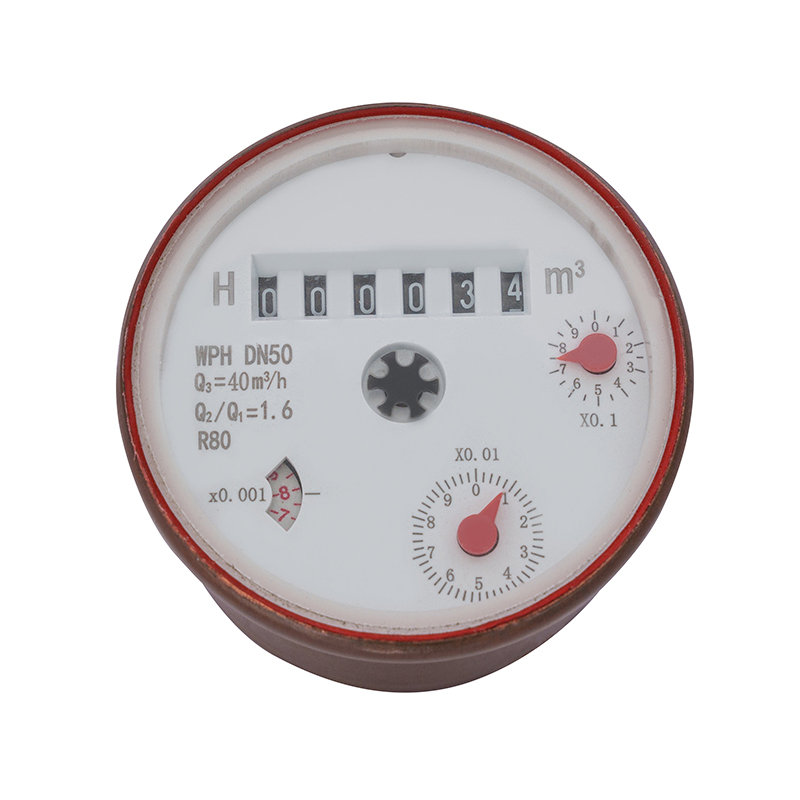
Hall Element Pulse Remote Transmission Sensor Assembly
As an active pulse sensor, the Hall element requires external power supply during operation. When the magnetic steel on ...
Start Our Cooperation!

Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. is China Industrial Water Meter Manufacturers and Custom Smart Water Meter Factory specializing in producing large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, including product design and development, mold manufacturing, injection molding processing, and assembly and verification. The industrial chain is complete and we have long-term cooperation with many domestic enterprises. Enterprise purpose: quality first, reputation first. Warmly welcome industry colleagues to visit and provide guidance.
-
Industry Standard
-
9+ Industrial Experience
-

Exported To Many Countries
-

7*24 Hours Customer Service
Recent News
Commercial Water Meter Manufacturers & Water Flow Meter Factory Guide for Accurate Metering
12-Mar-2026
How does the WI irrigation water meter adapt to different pressures and water flow rates?
05-Mar-2026
Does the WPH horizontal spiral wing water meter offer convenient connection interfaces?
26-Feb-2026
Does the WS vertical spiral wing water meter have anti-backflow, anti-impact design, or leakage protection mechanisms?
19-Feb-2026
Industry Knowledge
I. Understanding Water Meters: The Foundation of Metering Technology
1.1. Defining Water Meters and Their Core Function
A water meter is a crucial measuring instrument used to record the volume of water flowing through a pipeline. They serve as the cornerstone for water management, billing, and resource conservation efforts.
The core functions of a water meter include:
Accurate Measurement: Providing precise data for water consumption, ensuring fair and reasonable billing.
Resource Monitoring: Helping water utilities track consumption patterns across specific areas, commercial enterprises, or industrial facilities.
Leak Detection: Assisting in identifying and locating pipe leaks, either by comparing inflow and outflow or through real-time monitoring.
The reliability and accuracy of water meters directly impact a water utility's revenue assurance, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. For companies specializing in manufacturing large-diameter water meters and their core movements, like Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., the key competency lies in guaranteeing the precision and durability of the measurement. This is especially critical when dealing with high flow rates and complex applications.
Overview of Different Water Meter Types:
| Type | Working Principle | Primary Application |
| Mechanical | Utilizes the force of water flow to turn moving parts like turbines or pistons for volume measurement. | Residential, commercial, and certain industrial applications. |
| Electromagnetic | Based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, measuring the voltage generated by a conductive fluid flowing through a magnetic field. | Industrial use, wastewater treatment, and large-diameter metering. |
| Ultrasonic | Calculates flow velocity by measuring the time difference of ultrasonic signals propagating through the water. | Smart metering, high-accuracy applications. |
1.2. Why Choosing the Right Metering Technology Matters
Selecting the appropriate water metering technology is not just about choosing a device; it is a strategic decision that affects operational efficiency, cost control, and future development.
For Residential/Commercial Users: Measurement accuracy directly determines the user's bill, influencing customer relations.
For Industrial Users: Metering data is a critical input for process control and water use optimization; even minor errors can lead to significant operational losses.
For Water Utilities: Minimizing Non-Revenue Water (NRW) is a top priority for improving profitability and achieving sustainable management.
In this field, “Smart Water Meters” and “Industrial Water Meters” represent two distinct yet equally vital metering paths.
Smart Water Meters focus on data collection, communication, and customer engagement, serving as the foundation for building "smart cities."
Industrial Water Meters specialize in providing reliable, high-capacity measurement under extreme or high-flow conditions, acting as the safeguard for major infrastructure and production processes.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. is a company specializing in producing large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, offering a complete industrial chain including product design and development, mold manufacturing, injection molding processing, and assembly and verification. This complete industrial chain and strong team of experts allow the company to leverage the latest technology and accumulated experience to provide stable and reliable products for customers pursuing either intelligent data or demanding large-diameter high-precision metering. This full-spectrum capability has led to long-term cooperation with many domestic enterprises. The company's corporate mission is: Quality First, Reputation First.
II. Smart Water Meters: Data-Driven Intelligent Metering
2.1. Definition and Key Technologies of Smart Water Meters
Smart Water Meters are modern devices that integrate metering, data processing, storage, and two-way communication modules. They actively collect and transmit data, moving beyond passive recording to become a vital Internet of Things (IoT) endpoint in the water sector.
Core Characteristics of Smart Water Meters:
Real-time or High-Frequency Data Collection: Capability to record water usage at hourly, minute, or even higher frequencies.
Integrated Communication Modules: Equipped with radio frequency, cellular networks (e.g., NB-IoT, Cat-M), or fixed network modules for remote data transmission.
Remote Shut-off Capabilities (Optional): Allowing utilities to remotely control the flow of water for operational needs.
Understanding Automated Meter Reading (AMR) and Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI):
| Feature | Automated Meter Reading (AMR) | Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) |
| Communication Direction | Unidirectional (from meter to utility). | Bidirectional (meter and utility communicate with each other). |
| Data Frequency | Daily or less frequent, primarily used for billing. | Real-time or high-frequency (minutes/hours), used for analysis and control. |
| Function Focus | Enhances reading efficiency, replacing manual reading. | Enables advanced functions like remote control, real-time leak detection, and demand response. |
| Technology Base | Typically based on radio frequency technology read by handheld devices. | Based on fixed communication networks (e.g., cellular, Mesh networks). |
2.2. Core Functionality and Technical Advantages
Smart Water Meters provide significant technical advantages to water management through their advanced functions:
Real-time Data Monitoring and Analysis: Real-time data streams allow utilities to quickly identify anomalies in consumption patterns.
Leak Detection and Alert Mechanisms: This is a highly valued function. By monitoring continuous flow during low-demand periods (e.g., night), the smart meter can accurately locate small leaks on the customer side and in the system network. This shifts management from traditional leak control to preventive maintenance.
Remote Valve Control: Greatly improves service efficiency, allowing utilities to quickly handle shut-off requirements for non-payment, sudden leaks, or maintenance, enhancing customer service.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.’s complete industrial chain in water meter movement design and mold manufacturing is crucial for the long-term accuracy and reliability of smart water meters. The measurement precision of smart meters, whether based on mechanical principles with encoders or electronic principles like ultrasonic/electromagnetic, must rely on high-quality movements and structural components. Water Cube, utilizing its expertise and accumulated experience, ensures the high accuracy and durability of its products' core metering components, which is the basis for the long-term stable operation of smart water meters.
2.3. Applications and Benefits of Smart Water Meters
Smart water meters are more than just billing tools; they are efficient resource management terminals:
| Application Scenario | Key Benefit | Contribution Area |
| Residential and Commercial Use | Reduced water waste, improved customer engagement (users can view real-time consumption via apps). | Sustainability, customer relations. |
| Smart City Development | Enables refined and automated water resource management, optimizing supply network operations for better water resource management. | Urban infrastructure, macroeconomic benefits. |
| Water Utility Operations | Increases reading efficiency, significantly reduces Non-Revenue Water (NRW), and boosts revenue assurance. | Operational efficiency, financial health. |
2.4. Leading Smart Water Meter Technology Features
Encoder Technology: Converts mechanical water meter readings into digital signals for high-resolution, tamper-proof remote reading.
Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN): Utilizing NB-IoT or LoRa technologies, ensuring reliable, low-power data transmission even in remote or underground environments.
High/Low Flow Sensitivity: The ability to accurately detect even extremely low flow rates, such as continuous toilet leaks, is a critical technical foundation for the smart meter's leak detection.
Water Cube leverages its professional experience in large-diameter meters and movements, combining its high-quality mechanical metering foundation with these cutting-edge communication and sensing technologies to manufacture products that meet the market's dual demands for precision and intelligence.
III. Industrial Water Meters: Engineered for Harsh Environments and High Flow
3.1. Definition and Unique Requirements of Industrial Water Meters
In contrast to smart meters that focus on data communication and granular management, the core value of Industrial Water Meters lies in their ability to measure high flow rate capacity and ensure high durability under extreme conditions. They are indispensable metering instruments in large production facilities and critical infrastructure.
Unique Requirements of Industrial Water Meters:
High Flow Rate Capacity: Must accurately measure a wide range of very high flow rates, typically featuring larger pipe diameters.
Durable Construction: Built with robust materials (e.g., cast iron, stainless steel) and designs to withstand pipe vibrations, water hammer, and continuous high-pressure operation.
Suitability for Harsh Environments: Must handle challenging conditions such as wastewater, chemically corrosive fluids, or high temperatures.
Wider Measurement Range: Required to maintain high accuracy across the entire dynamic operating range.
As a company specializing in the production of large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. possesses a natural advantage in the industrial water meter sector. Manufacturing large-diameter meters demands not only sophisticated mold manufacturing and injection molding techniques but also a deep understanding of hydraulics and structural integrity. Water Cube ensures that its products, when handling extremely high flows, adhere to its corporate mission of Quality First, providing stable and reliable metering performance.
3.2. Core Technology and Reliability
Industrial water meters primarily rely on the following technologies, each designed to maximize their robustness and reliability and achieve accurate measurement of large water volumes.
| Industrial Meter Core Technology | Key Working Principle | Industrial Application Advantage |
| Electromagnetic | No moving parts, unaffected by fluid density or viscosity; only suitable for conductive fluids. | Applicable to wastewater, slurry, or fluids with solid particles; offers high reliability. |
| Ultrasonic | High accuracy, no pressure loss; clamp-on or insertion designs facilitate use on large-diameter pipes. | High accuracy, and can achieve minimal maintenance requirements. |
| Mechanical (Turbine/Propeller) | Suitable for clean, steady, high-flow conditions; simple structure, relatively low cost. | Applicable for agricultural irrigation or total factory intake measurement. |
Water Cube, with its profound research into water meter movements and complete industrial chain, ensures that the core components of both large mechanical and complex non-contact industrial meters meet industrial-grade standards for durability and precision. This complete industrial chain, from design and molding to assembly and verification, is the guarantee of product robustness and long-term reliability.
3.3. Key Application Areas of Industrial Water Meters
Industrial water meters play an irreplaceable role in locations involving large-scale water use:
Manufacturing Plants: Monitoring cooling water, process water, and wastewater discharge to achieve high efficiency in water resource utilization.
Agriculture: Measuring large water volumes distributed from the source to the fields, helping to optimize irrigation schedules and conserve water.
Wastewater Treatment Facilities: Monitoring inflow and outflow rates to ensure the efficiency and compliance of the treatment process.
Power Generation: Metering water usage in cooling towers, boilers, and steam cycles to ensure the safety and efficiency of high-pressure systems.
3.4. Leading Industrial Water Meter Technology Features
Full-Bore Design: Characteristic of electromagnetic meters, where the pipe diameter matches the sensor bore, resulting in no pressure loss—ideal for high-viscosity or suspended-solids fluids.
Wide Turndown Ratio: Ensures accurate measurement across a large dynamic range, regardless of whether the flow is extremely high or low during industrial process variations.
High Ingress Protection (IP Rating): Typically requires IP68, ensuring the device can resist moisture and dust ingress in outdoor or submerged installation environments.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. adheres strictly to the principle of Reputation First, gaining industry recognition by providing **large-diameter water meters** that meet these industrial-grade standards.
IV. Key Differences: Smart vs. Industrial Water Meters
4.1. Functionality and Focus
The fundamental design intent of these two meter types results in distinct functional priorities.
Smart Water Meters: The emphasis is on data collection, communication, and remote control. They are information collectors designed for intelligent, refined management and optimization of customer service within the water network.
Industrial Water Meters: The focus is on measuring large volumes and durability. They are reliable "workhorses," ensuring continuous, accurate flow data under harsh operating conditions, with data transmission often being a secondary or supplementary function.
4.2. Technology Comparison
The difference in technical foundation is the most important factor distinguishing these two meter types.
| Comparative Feature | Smart Water Meters | Industrial Water Meters |
| Metering Principle | Focused on ultrasonic, electromagnetic, or mechanical with encoders. | Focused on high-performance electromagnetic, ultrasonic, or large-diameter turbine. |
| Communication Technology | Utilize advanced sensors, communication modules, and software (e.g., NB-IoT, LoRa, AMI/AMR). | Typically use pulse output, 4-20mA signal output, or integrate Industrial IoT (IIoT) gateways for data transfer. |
| Power Supply | Mostly rely on battery power (requiring ultra-low-power design). | Mostly rely on external power supply (industrial grid or solar). |
| Key Focus | Real-time data, remote control, leak detection, customer interaction. | Robustness, wide turndown ratio, corrosion resistance, large volume measurement. |
4.3. Applications and Environmental Conditions
Their intended application environment dictates their design parameters, such as IP rating and pressure tolerance.
Smart Water Meters: Suited for residential, commercial, and smart city applications. Typically installed in protected environments, such as meter boxes or indoors.
Industrial Water Meters: Ideal for industrial processes, agriculture, and water treatment. Designed to withstand high pressure, high temperature, vibration, and water flow that may contain impurities or corrosive media.
4.4. Cost, Lifespan, and Maintenance Cycle Considerations
| Consideration Factor | Smart Water Meters | Industrial Water Meters |
| Upfront Cost | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology. | Lower initial cost (for mechanical types); non-contact, high-precision meters can also be costly. |
| Operating Cost | Low: Reduced labor and water loss costs due to remote reading and leak control. | Moderate to High: May require more on-site calibration or repair, potentially necessitating more maintenance. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Achieved through long-term returns by reducing NRW and improving operational efficiency. | Ensures returns by guaranteeing measurement accuracy and reliability for production processes. |
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., with its professional capability in the design and manufacturing of large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, is able to provide products with a high degree of robustness and reliability, whether for the durable movements required in industrial settings or the high-precision movements foundational to smart meters. The company's complete industrial chain and commitment to Quality First ensure that customers receive high-quality core component support regardless of the chosen metering solution.
V. How to Choose the Right Water Meter: Smart or Industrial?
5.1. Factor 1: Flow Rate and Accuracy Requirements
The project's water usage characteristics are the primary factor determining the meter type.
Flow rate requirements:
If you need to measure extremely high instantaneous flows, or if the pipe diameter is large (e.g., main pipes DN100 and above, industrial intake), you should prioritize the high flow rate capacity design of Industrial Water Meters, particularly electromagnetic or large turbine meters.
If the flow is small but highly variable, and low-flow leak detection is critical, Smart Water Meters (especially ultrasonic or those with high-resolution encoders) excel in low-flow sensitivity.
Accuracy needs:
For critical process metering in industrial applications, extremely high accuracy and repeatability are often required, making high-precision Industrial Water Meters (e.g., electromagnetic) the preferred choice, conforming to industrial standards.
Smart meters can also achieve excellent billing accuracy in residential and commercial settings through high-frequency data sampling and remote calibration.
5.2. Factor 2: Budget Constraints and ROI
The decision is not only technical but also an economic assessment.
Budget constraints:
If the budget is very limited and real-time data or remote functions are not necessary, traditional mechanical Industrial Water Meters (especially large-diameter) may offer a lower initial cost.
Smart Water Meters have a higher upfront cost, but their long-term benefits must be calculated, such as significantly reduced Non-Revenue Water (NRW), lower manual reading costs, and improved asset management.
Data monitoring requirements:
If you require real-time alerts, usage analysis, load profiles, or remote shut-off capability, investing in Smart Water Meters with AMI functionality is essential.
If only periodic total volume data is needed for monthly billing or compliance reports, the simple pulse output of an Industrial Water Meter may suffice.
5.3. Factor 3: Environmental and Installation Conditions
The installation location and fluid medium have a decisive impact on meter selection.
Environmental conditions:
In industrial environments with poor water quality, impurities, or fluctuating temperature/pressure, the durable construction and corrosion resistance of Industrial Water Meters are mandatory. Non-contact electromagnetic or ultrasonic meters are ideal choices.
Smart meters usually operate in cleaner water environments, but if installed outdoors, they must also have a high Ingress Protection rating (e.g., IP68).
Installation location:
For difficult-to-access, remote, or underground installations, the remote communication capability of a Smart Water Meter (e.g., based on LPWAN) provides the only effective solution.
5.4. Consulting with Experts and Customized Solutions
Professional consultation and customized services are crucial for complex industrial processes or large-scale smart city deployments.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., specializing in large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, provides precise advice and customized solutions, backed by its complete industrial chain in product design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, and assembly and verification, along with a strong team of experts.
Whether your project requires the robustness and durability and accurate measurement of large water volumes of an Industrial Water Meter, or the real-time data analysis capabilities of a Smart Water Meter, Water Cube utilizes its accumulated experience and corporate mission of Quality First, Reputation First to ensure that the delivered metering products perfectly match your specific requirements, achieving optimal ROI and water resource management efficiency. We warmly welcome industry colleagues to visit and provide guidance.
VI. Future Trends in Water Metering
6.1. Deepening Integration of IoT and AI
Future metering systems will no longer be isolated devices but highly interconnected and intelligent network nodes.
Smart Water Meters:
AI-Powered Advanced Data Analysis: AI and machine learning algorithms will enable faster and more accurate identification of complex leak patterns, fraud, and consumption anomalies. This allows Smart Water Meters to play a larger role in reducing water waste.
Edge Computing: Shifting some data processing capability to the meter itself, allowing for real-time anomaly detection and alerting locally, reducing reliance on the cloud and speeding up response times.
Industrial Water Meters:
IIoT Empowerment: High-precision Industrial Water Meters will be more widely integrated with IIoT gateways, seamlessly feeding their reliable, high-flow metering data into factory SCADA systems and cloud platforms. This facilitates real-time monitoring and automated control of industrial processes.
Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing AI to analyze meter operational data (e.g., battery voltage, signal strength, calibration drift) to predict when maintenance or replacement is needed, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
6.2. Sustainability and Water Conservation
Amid climate change and increasing water scarcity, both meter types will be critical tools for achieving global water conservation goals.
Smart Water Meters:
Driving Behavior Change: Through real-time, highly granular consumption data feedback mechanisms, Smart Water Meters can significantly raise user awareness and engagement, thereby promoting water conservation behavior both publicly and individually.
Improving Non-Revenue Water (NRW) Management: By accurately locating and quantifying leaks, they greatly enhance utility efficiency in better water resource management.
Industrial Water Meters:
Optimizing Industrial Water Efficiency: By precisely monitoring cooling water, boiler feed water, and process water, Industrial Water Meters help industrial users identify and quantify high-consumption stages in their processes, driving the adoption of water-saving technologies and water recycling systems.
6.3. Increasing Standardization and Interoperability
The future will bring greater focus on interoperability, ensuring that Smart Meters and Industrial Meters from different manufacturers can seamlessly integrate into the same management platform.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., with its complete industrial chain, plays an important role in this trend. The company's professionalism in water meter movements, mold manufacturing, and assembly verification allows it to rapidly adapt to evolving communication and sensing technology standards.
Through its deep experience in large-diameter water meter manufacturing, Water Cube can provide highly reliable and durable core metering components for IIoT-enabled Industrial Water Meters.
By integrating the latest communication technology, Water Cube ensures that the core components of its Smart Water Meters maintain advantages in high accuracy and low power consumption.
Water Cube is committed to providing reliable, future-proof metering solutions by leveraging the latest technology and accumulated experience, all while adhering to its corporate mission of Quality First, Reputation First.
VII. FAQ
Q 1: What is the typical battery life of Smart Water Meters?
A: The battery life of a Smart Water Meter is a crucial design consideration, as it directly impacts operational costs and maintenance cycles.
Generally, Smart Water Meters based on Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN, such as NB-IoT or LoRaWAN) are designed to have a battery life between 5 and 15 years.
Battery life depends on the frequency of data transmission, the signal strength of the communication environment (weaker signals consume more power), and whether high-power functions like remote control (valve operation) are utilized.
Selecting high-quality water meter movements and efficient circuit design is fundamental to extending battery life. For example, the precision and low power requirements in Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.'s water meter movement designs help minimize the metering module's power consumption, optimizing overall battery longevity.
Q 2: How can the accuracy of Industrial Water Meters be ensured in harsh environments?
A: Harsh conditions (such as high pressure, high temperature, or fluids containing solids or corrosive media) pose significant challenges to the accuracy of Industrial Water Meters. The main methods to ensure accuracy include:
Selecting the Appropriate Metering Principle: In environments with solid particles and corrosive fluids, non-contact meters like electromagnetic or ultrasonic meters should be prioritized, as they have no moving parts and are less susceptible to wear.
High-Standard Materials and IP Rating: Using high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., stainless steel or specialized coatings) and high Ingress Protection ratings (e.g., IP68) for the casing is essential to guarantee robustness and reliability.
Regular Calibration: Although Industrial Water Meters are designed to be rugged, periodic on-site or laboratory calibration is still necessary, according to industry standards or manufacturer recommendations, to maintain long-term accuracy.
Q 3: What is the main difference between AMR and AMI?
A: Both AMR (Automated Meter Reading) and AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) fall under the umbrella of smart metering, but they differ fundamentally:
| Comparative Feature | Automated Meter Reading (AMR) | Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) |
| Communication Direction | Unidirectional: Meter transmits data to the meter reader or data center. | Bidirectional: Data center can send commands to the meter (e.g., remote control). |
| Real-time Capability | Low: Typically daily or weekly data transmission. | High: Can achieve minute- or hour-level real-time data transmission. |
| Functionality | Limited to remote reading and data collection. | Includes advanced functions like remote control, leak detection, and firmware upgrades. |
The AMI system is better positioned to realize the full potential of Smart Water Meters, enabling better water resource management.
Q 4: Are there national or industry standards for water meter replacement?
A: Yes. In most countries and regions, water meters are considered mandatory verifiable measuring instruments.
There are strict legal regulations and industry standards governing the initial verification and subsequent re-verification/replacement cycle of water meters.
Typically, the mandatory replacement cycle is based on the meter type, diameter, and local regulations (e.g., every 6 or 8 years).
Both Smart Water Meters and Industrial Water Meters must comply with national accuracy class requirements upon installation and replacement. Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. prioritizes Quality First, ensuring that all manufactured large-diameter water meters and water meter movements strictly adhere to domestic and international metering standards.
Q 5: Should small businesses choose Industrial Water Meters?
A: Not necessarily. Small businesses should base their choice on their volume of consumption and the nature of their water use:
If the water consumption is high and the pipe diameter is large (e.g., small manufacturing or car washes), or if the water flow environment is complex, then Industrial Water Meters may be required to ensure accurate measurement of large water volumes and durability.
If the water consumption is comparable to a large commercial building and the business is more concerned with remote monitoring, leak detection, and refined management (e.g., a chain restaurant), then a Smart Water Meter is more suitable.
The final choice should be based on a comprehensive assessment of flow rate requirements and data monitoring requirements.



 عربى
عربى