Provide Customers With High-Quality Water Meter Products
Custom Horizontal Water Meter Manufacturers
-

WPH-DN40-DN65WPH horizontal spiral wing water meter
Summary 1. Record the total amount of water flowing through the tap water pipeline. Cannot be used for measuring sewage ... -

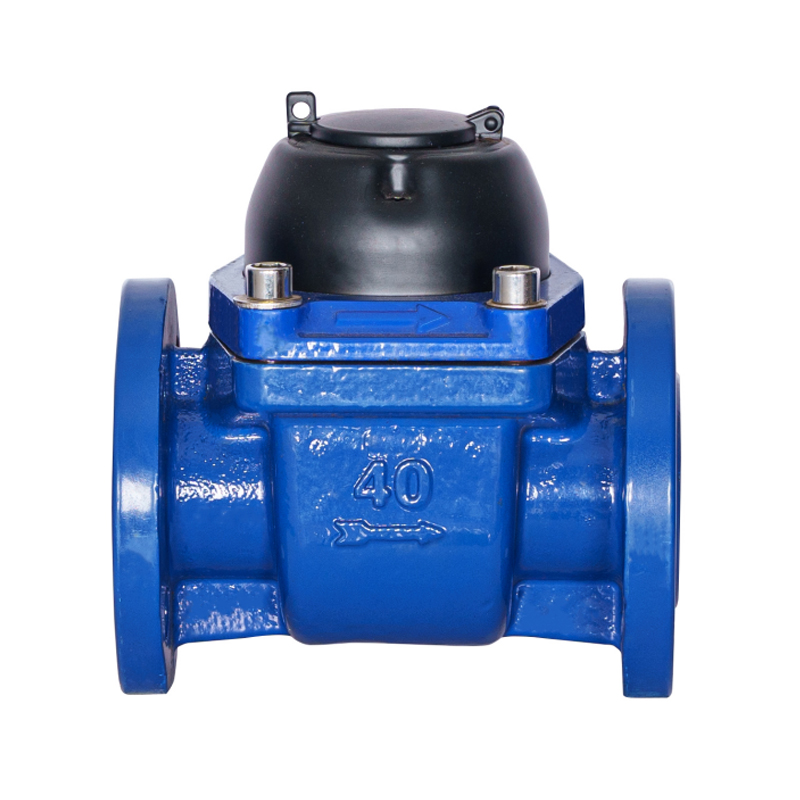
WPH DN50-DN200 Horizontal Detachable Spiral Wing Water Meter
Due to the product structure and optimized impeller fluid dynamic floating design, our new generation wide range horizon... -

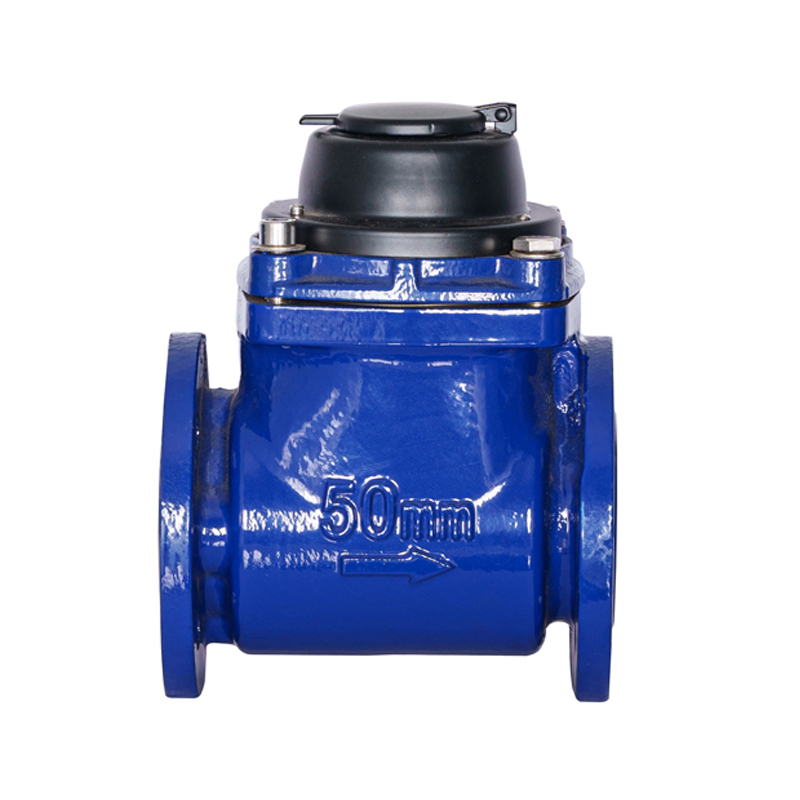
WPH DN50-DN200 Horizontal Detachable Screw Wing Non-Magnetic Integrated Water Meter
Structural Design Adopts a horizontal screw wing structure with the rotating shaft parallel to the water flow direction.... -
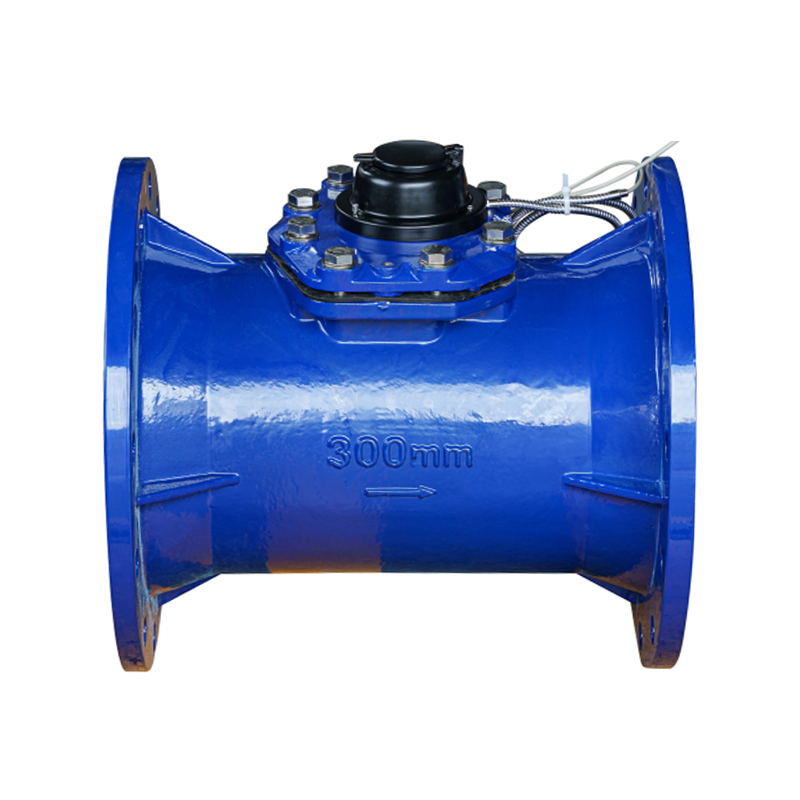

LXLC-DN50-DN500 Horizontal Detachable Water Meter
Summary 1. Record the total amount of water flowing through the tap water pipeline. Cannot be used for measuring sewage ... -
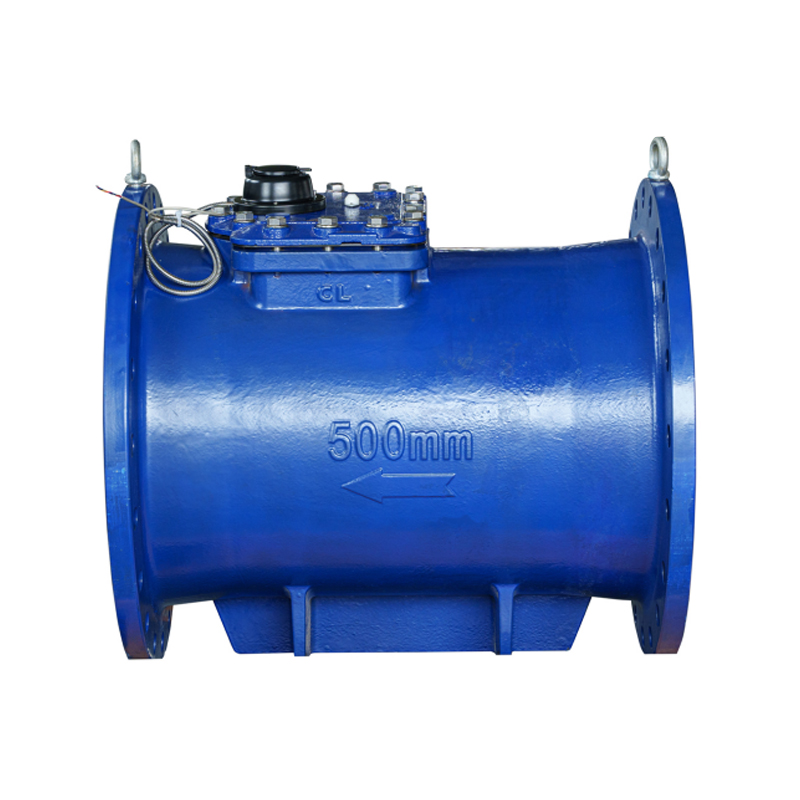

DN400-600 Horizontal Removable Water Meter
1. It records the total water consumption flowing through the tap water pipeline. It cannot be used for metering sewage ... -
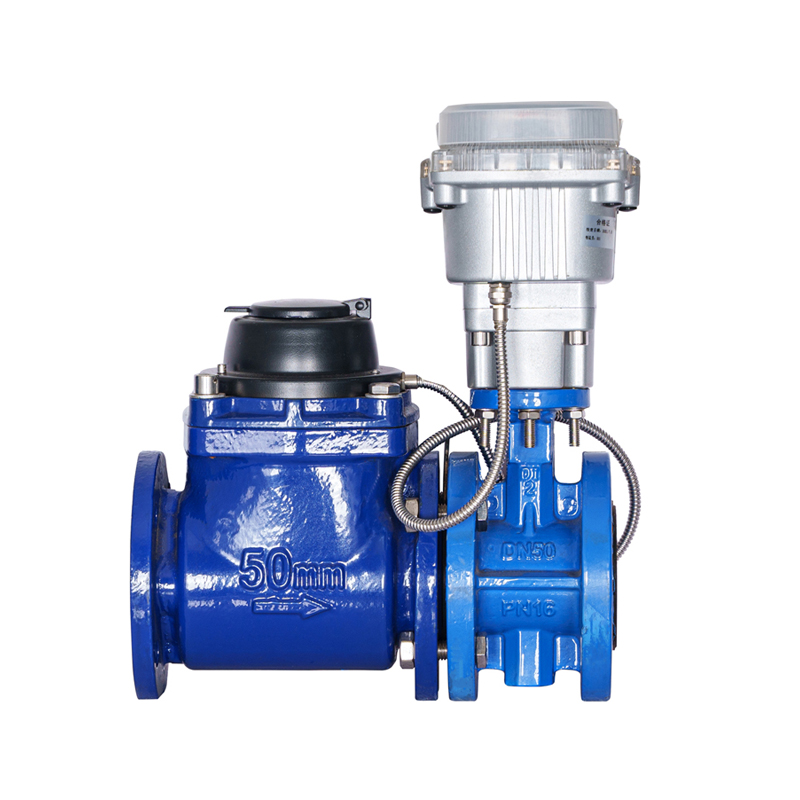

WPH DN50-DN200 Horizontal Detachable Screw Wing Valve-Controlled Water Meter (with Stacked Valve)
This water meter is a LORA Remote Smart Water Meter, featuring 4G wireless & NB-IoT remote meter reading, valve cont...
Start Our Cooperation!

Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. is China Horizontal Water Meter Manufacturers and Custom WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter Factory specializing in producing large-diameter water meters and water meter movements, including product design and development, mold manufacturing, injection molding processing, and assembly and verification. The industrial chain is complete and we have long-term cooperation with many domestic enterprises. Enterprise purpose: quality first, reputation first. Warmly welcome industry colleagues to visit and provide guidance.
-
Industry Standard
-
9+ Industrial Experience
-

Exported To Many Countries
-

7*24 Hours Customer Service
Recent News
Commercial Water Meter Manufacturers & Water Flow Meter Factory Guide for Accurate Metering
12-Mar-2026
How does the WI irrigation water meter adapt to different pressures and water flow rates?
05-Mar-2026
Does the WPH horizontal spiral wing water meter offer convenient connection interfaces?
26-Feb-2026
Does the WS vertical spiral wing water meter have anti-backflow, anti-impact design, or leakage protection mechanisms?
19-Feb-2026
Industry Knowledge
1. In-Depth Look at the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
1.1. Definition and Basic Working Principle of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
The WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is a large-volume velocity water meter widely used for metering in industrial, commercial, and main pipelines. Its primary function is to measure the total volume of cold (or hot) water flowing through a closed, fully-filled pipe.
The term "Horizontal" refers to its installation orientation, where the meter's main axis is parallel to the pipeline axis, ensuring horizontal mounting. The "Spiral Wing" describes its core metering principle:
Working Mechanism: As water flows into the meter's measuring chamber, it radially impacts the spiral wing (impeller) positioned at the center of the chamber. The kinetic energy of the water drives the spiral wing to rotate rapidly around its main axis.
Flow Correlation: Within a specific flow range, the angular velocity of the spiral wing is directly proportional to the volumetric flow rate passing through the meter.
Data Display: The rotation of the spiral wing is transmitted via a mechanical gear mechanism to a sealed register, which accumulates and displays the total volume of water that has passed through the meter.
The WPH meter design is particularly suited for large-diameter pipes and high flow measurement requirements, offering high throughput capacity and low head loss.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. is a company specializing in producing large-diameter water meters and water meter movements. With a strong team of experts, complete industrial chain (including product design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, and assembly and verification), and long-term cooperation with many domestic enterprises, the company utilizes its latest technology and accumulated experience to provide precise and reliable WPH metering solutions, adhering to its enterprise purpose: "quality first, reputation first."
Brief history and evolution of water meters:
Since their inception in the mid-19th century, water meters have evolved from simple positive displacement types to velocity types and modern smart meters. The spiral wing meter, as a crucial branch of velocity meters, was developed specifically to meet the demand for large-flow, trunk pipeline metering in urban development, significantly advancing the industrialization and refinement of water resource management.
1.2. Core Components and Their Functions
WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter consists of several key components that work together to ensure accurate and reliable measurement:
| Core Component | Primary Function | Impact on Metering Performance |
| Body | Holds all internal components, withstands pipeline pressure, and defines the flow path. | Material selection affects pressure rating and corrosion resistance. |
| Measuring Chamber | Guides the water flow to impact the spiral wing uniformly and smoothly, essential for accurate metering. | Chamber design directly influences flow velocity distribution and impeller rotation stability. |
| Spiral Wing | Core measuring element, driven by water flow; its speed is proportional to the water volume. | The material, balance, and blade angle of the wing determine the meter's accuracy class. |
| Transmission Mechanism | Transfers the rotation of the spiral wing to the register, often via magnetic coupling or gears. | Transmission accuracy and friction are critical factors affecting low-flow accuracy. |
| Register / Display | Display component, accumulates and stores the total measured water volume data. | Can be dry type (magnetic coupling, reading mechanism isolated from water) or wet type (reading mechanism submerged). |
Influence of Spiral Wing Design on Measurement Accuracy:
The number of blades, pitch angle, and the lightness and durability of the spiral wing material directly determine the meter's sensitivity to flow starting (initial flow rate) and its stability at high flow rates. A well-designed spiral wing ensures a linear relationship between its rotation speed and the water flow rate across a wide range, which is fundamental to achieving high accuracy classes (e.g., as required by ISO 4064).
Types of Register: Dry Type vs. Wet Type:
Dry Type Register: Uses magnetic coupling to transfer rotation to the counter, isolating the counter from the water flow.
Advantages: Clear reading, less affected by water quality (e.g., silt, scale), prevents internal condensation.
Application: Suitable for poor water quality or environments requiring high reading clarity.
Wet Type Register: The counter is submerged in the water, transmitting rotation directly via mechanical gears.
Advantages: High transmission reliability, generally simpler structure.
Application: Suitable for better water quality environments.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.'s complete industrial chain ensures the manufacturing quality and matching precision of key components, from the measuring chamber to the spiral wing and register, thus guaranteeing the exceptional performance of their WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters.
2. Key Features and Benefits of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
2.1. Superior Measurement Performance and Reliability
Accuracy and reliability in measurement: The WPH meter is designed for precise measurement of large flows. Its flow channel is typically straight-through, reducing water turbulence and stabilizing the linear relationship between impeller speed and actual flow rate. This allows the meter to maintain very high accuracy around the Permanent Flow (Q3), ensuring fairness in water billing and distribution.
Durability and long lifespan: WPH meters are constructed using robust materials for the casing and critical internal parts. The manufacturing expertise of Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., supported by its complete industrial chain, ensures the high precision and consistency of these components, which is vital for the meter's long-term operational stability and extended service life. The specially designed bearing system withstands the wear and tear from long-term, high-speed rotation, significantly reducing failure rates and replacement frequency.
2.2. Structural Design and Hydrodynamic Advantages
Wide flow range and its importance: The WPH meter offers a broad range of flow measurement, especially for high flows and large-diameter pipes. This means it can accurately measure both normal supply flows and handle sudden large flows (e.g., for fire fighting or instantaneous high demand). The wide flow range allows a single model to cover a wider spectrum of operating conditions, simplifying selection.
Low head loss benefits for the water supply system: Because the WPH meter's flow path is typically axial (straight-through), flow resistance is minimal, resulting in extremely low head loss. Low head loss is economically beneficial, as it maintains effective pipeline pressure and flow without increasing pump energy consumption, which is critical for long-distance transmission lines or industrial systems requiring stable pressure.
2.3. Materials and Environmental Adaptability
Resistance to corrosion and wear: The meter casing and water-contacting components often use high-quality materials such as cast iron, copper alloy, or stainless steel, offering excellent corrosion resistance. Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.'s specialization in water meter movement production includes using advanced polymer composite materials for the spiral wing. These materials are not only lightweight and sensitive but also resistant to wear and scale buildup. This material selection significantly enhances the meter's adaptability and lifespan in various water quality environments.
2.4. Modern Technology Integration and Operational Convenience
AMR/AMI compatibility: Integration for remote metering: Modern WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters are usually equipped with pulse output interfaces or reserved space for communication modules, allowing easy integration into Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) or Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems.
Advantage: This enables remote data acquisition, real-time monitoring, and big data analysis, dramatically improving reading efficiency, reducing labor costs, and aiding in the rapid detection and localization of network leaks.
Easy installation and maintenance design features: WPH meters typically use flange connections for fast and convenient installation. Their structural design also prioritizes easy maintenance. For example, some models feature a removable measuring element (movement), allowing the core metering unit to be serviced or replaced without removing the entire body from the pipeline, minimizing water shutdown time and simplifying maintenance procedures.
Summary of Comparative Parameters (Highlighting WPH Advantages):
| Feature | WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Meter (Large Flow) | Typical Positive Displacement Meter (Small Caliber) |
| Main Application | Main supply lines, industrial, commercial large-flow metering | Residential users, small branch metering |
| Head Loss | Extremely Low | Higher |
| Flow Range | Wide Flow Range, excellent high-flow performance | Narrower, better suited for low flow and starting flow |
| Structural Feature | Horizontal straight-through flow path, axial spiral wing rotation | Complex measuring chamber, volumetric metering |
| Advantage | Strong metering capacity, low pressure loss, wide applicability | Low starting flow, high low-flow accuracy |
3. Technical Specifications and Standards of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
3.1. Size, Flow Rate, and Pressure Parameters
Available sizes and flow rates: WPH meters are primarily designed for large-caliber pipelines, with Nominal Diameters (DN) typically starting from DN50 and covering large calibers such as DN80, DN100, DN150, up to DN300 and beyond. Flow parameters are defined according to ISO 4064 standards:
Overload Flow (Q4): The maximum flow rate at which the meter can operate for a short period.
Permanent Flow (Q3): The recommended flow rate for the meter's long-term, stable operation.
Transitional Flow (Q2): The flow point that divides the high-accuracy zone and the low-accuracy zone (typically ±2% and ±5% error).
Minimum Flow (Q1): The lowest flow rate that the meter can accurately measure.
| Nominal Diameter (DN) | Permanent Flow (Q3) (m³/h) (Typical) | Overload Flow (Q4) (m³/h) (Typical) | Applicable Scenarios |
| DN 50 | 15 - 25 | 18.75 - 31.25 | Medium commercial or small industrial |
| DN 100 | 60 - 100 | 75 - 125 | Large commercial buildings or city network branches |
| DN 200 | 250 - 400 | 312.5 - 500 | Industrial main pipelines or water plant outlets |
Pressure ratings: The meter's Nominal Pressure (PN) indicates the maximum sustained working pressure it can withstand. Common pressure ratings include PN10 (1.0 MPa), PN16 (1.6 MPa), and PN25 (2.5 MPa). The high-pressure rating ensures that WPH meters can be safely used in high-pressure urban supply systems and industrial high-pressure lines.
3.2. Accuracy Class and Environmental Requirements
Accuracy class (e.g., Class A, Class B) interpretation: Based on international standards ISO 4064 (or OIML R49), water meters are classified into different accuracy classes according to the Maximum Permissible Error (MPE) over their specified flow range. WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters typically achieve high accuracy classes to meet strict metering requirements.
Temperature ranges limitations: Meters are categorized into cold water and hot water types. Standard WPH cold water meters typically operate from 0.1°C to 30°C or 50°C; WPH hot water meters can handle temperatures up to 90°C or higher, suitable for metering in industrial heat supply or central heating systems.
3.3. Structural Materials and Compliance
Material specifications (e.g., brass, stainless steel) and their impact on lifespan:
Casing: Large-caliber WPH meters typically use cast iron or ductile iron with an anti-corrosion coating; smaller calibers or applications with high water quality requirements may use copper alloy or stainless steel.
Internal Components: Key components like the spiral wing, bearing supports, and bearings use wear-resistant, low-friction engineering plastics or stainless steel to ensure metering accuracy and longevity.
Standards compliance (e.g., ISO 4064): Importance of international general standards: The design, manufacturing, and inspection of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter must strictly comply with international and national metering standards, such as:
ISO 4064 / OIML R49: General technical requirements for drinking water cold and hot water meters.
National Standards: Corresponding mandatory metering regulations exist in various countries.
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. guides its product design, development, and verification processes by these stringent international and domestic standards. The company’s robust expert team and complete industrial chain ensure that every WPH water meter product's metering performance, pressure capacity, and durability meet or exceed compliance requirements.
4. Wide Application Scenarios of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
4.1. Urban Water Supply and Metering
Role in Residential water metering: While WPH meters are mainly for large-caliber applications, they play a critical role as the basic meter for calculating apportionment in the main inlet pipe of large residential areas or high-rise buildings. They accurately measure the total water volume entering the entire community, serving as the basis for settlement between the water company and property management.
Key measurement points in Water distribution networks: WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters are primary metering instruments in water distribution networks, widely installed at:
Water plant outlet main pipes.
Inlets of District Metering Areas (DMAs).
Large transmission trunk lines.
Data from these points is crucial for monitoring network flow, balancing pressure, and implementing Non-Revenue Water (NRW) control.
4.2. Commercial, Industrial, and Professional Sectors
Commercial and industrial water metering: Requirements for high flow and continuous measurement: Large factories, power stations, shopping centers, airports, and hospitals, and similar venues typically require high-volume water supply with significant fluctuations in demand. WPH meters reliably measure the total water consumption in these locations thanks to their wide flow range and robust structure.
Industrial Applications: Cooling water systems, boiler feed water, process water, etc.
Commercial Applications: Central air conditioning system makeup water, fire protection system monitoring.
Agricultural irrigation: Large flow monitoring and water resource management: In large-scale agricultural irrigation projects, massive water volumes are transferred from pump stations to irrigation areas. WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters can be installed at pump station discharge mains or inlets of large distribution canals to accurately monitor and control water abstraction, forming the foundation for implementing water rights allocation and efficient water resource utilization policies.
4.3. Smart Water and Water Resource Management
Data support role in Water resource management: In the context of building smart water systems, WPH meters through their AMR/AMI compatibility, provide high-frequency, reliable flow data. This data is the decision-making foundation for water departments to forecast usage, optimize scheduling, and formulate conservation policies.
As a component of smart water meter solutions: Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in large-caliber water meter movements and complete meter assembly, and can supply WPH products with pulse output or digital communication modules based on customer needs. The company ensures its products integrate seamlessly into various complex smart metering networks, assisting customers in achieving refined water management goals.
Comparison of Flow Characteristics for WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Meters in Different Applications:
| Application Scenario | Typical Caliber Range (DN) | Flow Characteristics | WPH Water Meter Advantage |
| City Trunk Lines | DN150 - DN300+ | Large and stable flow, requiring long-term continuous operation | High-pressure resistance, low head loss, strong durability |
| Large Industrial Parks | DN80 - DN200 | Flow fluctuation is large, instantaneous peaks are high | Wide flow range, ensuring high accuracy at peak flows |
| Agricultural Irrigation | DN100 - DN250 | Seasonal large flow, potentially poor water quality | Robust structure, certain resistance to impurities |
| Community Master Meter | DN50 - DN100 | Flow has clear periodicity (day/night changes) | Relatively low starting flow, stable transitional point |
Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. adheres to the enterprise purpose of "quality first, reputation first." Its complete industrial chain guarantees the reliability and accuracy of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter in these demanding applications, earning the favor of a wide range of customers.
5. Installation Guidelines for the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
5.1. Pre-installation Checks
Pre-installation checks:
Specification Verification: Check that the meter's Nominal Diameter (DN), pressure rating (PN), and flow parameters match the pipeline system design requirements.
Pipe Flushing: Before installing the meter, the pipeline must be thoroughly flushed to remove welding slag, silt, hemp fibers, or other debris. These are a primary cause of spiral wing jamming or premature bearing wear.
Accessory Inspection: Check that the accompanying flanges, sealing gaskets, and fasteners are intact.
Proper meter orientation and placement:
Orientation: The casing of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is usually cast with an arrow indicating the direction of water flow. Installation must ensure that the flow direction is exactly consistent with the arrow.
Placement: The WPH meter must be installed horizontally, with the dial face up. Tilted installation can cause uneven axial load on the spiral wing, severely affecting metering accuracy and lifespan.
Straight Pipe Segment Requirement: To ensure stable and uniform flow before entering the measuring chamber, a straight pipe segment of no less than 10D (where D is the pipe diameter) should be maintained upstream of the meter, and no less than 5D downstream.
5.2. On-Site Installation Procedures
Connecting to pipelines details and precautions:
Alignment: Ensure the meter's center axis is aligned with the pipeline's center axis. Forcing the meter into place by strongly stretching or bending the pipe is strictly prohibited.
Sealing: Use the matching flanges and high-quality sealing gaskets, tightening the flange bolts evenly and symmetrically.
Valve Installation: It is recommended to install a shut-off valve (or gate valve) both upstream and downstream of the meter for convenient future inspection, replacement, or cleaning without affecting the entire system operation.
Methods for Avoiding airlocks and backflow:
Airlocks: Air trapped in the pipeline can affect metering accuracy. When installing or initially filling the pipe, slowly open the upstream valve to allow water to fill the pipe gradually, and ensure all air is fully discharged through a vent valve.
Backflow: In some situations, a check valve may be required to prevent water flow reversal. Although check valves slightly increase head loss, they are necessary to prevent the meter from running backward or to maintain water quality integrity.
5.3. Commissioning and Testing
Commissioning and testing:
Slow Pressurization: The initial water flow must be introduced very slowly to avoid instantaneous shock damage to the spiral wing.
Inspection: Confirm that the meter runs smoothly at the Minimum Flow (Q1) and Permanent Flow (Q3), that the register indicates correctly, and that all connections are free of leaks.
Ex-factory and Installation Quality: Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. operates with a complete industrial chain, adhering to high standards from product design and development to final assembly and verification. This guarantees that every WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter leaving the factory possesses excellent inherent quality. The company advises users to strictly follow installation instructions to ensure the meter's superior performance is fully realized.
6. Maintenance and Troubleshooting of the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter
6.1. Routine Maintenance and Upkeep
Importance of Regular inspection and cleaning:
External Inspection: Periodically check the meter casing, connection flanges, and dial glass for signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks.
Operational Status Check: Listen to the meter's running sound; a normal WPH meter should operate smoothly with low noise.
Reading Record: Regularly record readings to promptly detect abnormal consumption patterns or potential metering failures.
How to prevent scale and impurities from affecting the spiral wing: In areas with poor water quality or high hardness, suspended solids or mineral deposits (scale) can adhere to the spiral wing blades or bearings, increasing frictional resistance, which leads to a higher starting flow rate and inaccurate metering. Regular pipeline flushing or installing an appropriate filter upstream of the meter are effective measures to prevent such issues.
6.2. Accuracy Maintenance
Calibration procedures: Ensuring long-term operational accuracy:
Legal Requirements: Many regions mandate periodic verification cycles (usually several years) for meters used for trade settlement. Upon expiration, the meter must be sent to an accredited metrology institution for re-verification or calibration.
On-site Verification: Some large WPH meters allow for on-site flow verification to confirm that the error at the main flow points remains within the Maximum Permissible Error (MPE) limit.
When to require re-verification of metering performance: Calibration or replacement is immediately recommended if any of the following occur:
Readings are significantly abnormal (large deviation from historical consumption data).
The meter stops rotating when flow is expected.
The meter rotates by itself when there is no flow (a rare occurrence).
6.3. Common Issue Resolution
Identifying and resolving common issues (e.g., leaks, inaccurate readings):
| Common Fault Phenomenon | Possible Cause | Solution |
| External Leakage | Loose flange bolts, damaged sealing gasket, casing cracks. | Retighten bolts, replace new sealing gasket, replace the entire meter if the casing is damaged. |
| High flow but inaccurate reading | Spiral wing stuck or severely worn, transmission system failure. | Inspect and clean the spiral wing or transmission parts; replace the movement or the entire meter if wear is severe. |
| Meter not rotating | Pipeline severe blockage, spiral wing jammed by large debris. | Check upstream and downstream valves, close them, and open the meter for cleaning. |
| Meter running backward | Backflow phenomenon (usually in multi-pump systems or elevated tanks). | Check and install a check valve. |
Replacement and repair guidelines: For WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meters, if the internal measuring element is damaged and the meter features a removable movement structure, only the movement can be replaced. This significantly reduces maintenance costs and water shutdown time.
The company Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. guarantees that its WPH water meter movements offer high precision and interchangeability. Using original or high-quality replacement movements supplied by the company during repairs is key to restoring the meter's performance to factory standards and maintaining the "quality first, reputation first" commitment.
7. Advantages Over Other Types of Water Meters
7.1. Internal Velocity Meter Comparison
Spiral wing meters are primarily divided into Horizontal (WPH) and Vertical (WPV) types, based on the relationship between the spiral wing axis and the water flow direction.
| Feature Comparison | WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Meter | WPV Vertical Spiral Wing Meter |
| Main Application | Large caliber, main pipeline, high flow metering | Small to medium caliber, large flow fluctuations, need for good starting flow |
| Flow Channel Structure | Axial straight-through, flow impacts the side of the spiral wing blades | Radial entry, flow turns to impact the spiral wing |
| Head Loss | Extremely Low | Slightly Higher (due to flow turn) |
| Flow Range | Large Permanent Flow (Q3), excellent high-flow performance | Smaller Permanent Flow (Q3), more sensitive to low flow |
| Impurity Resistance | Stronger (straight-through channel less prone to clogging) | Weaker (impurities can accumulate at the turn) |
7.2. Comparison with Positive Displacement Meters
Comparison with positive displacement meters: Positive displacement meters (like oscillating piston or rotary vane types) measure by repeatedly filling and emptying a fixed-volume measuring chamber. They are mainly used for small calibers and residential metering.
| Comparison Metric | WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Meter (Velocity Type) | Positive Displacement Meter |
| Metering Principle | Indirectly measures volume based on flow velocity and spiral wing speed | Directly measures volume based on fixed volume chambers |
| Minimum Flow (Qmin) | Moderate | Extremely Low (most sensitive to drips) |
| Head Loss | Low | High (large loss passing through complex chambers) |
| Caliber and Flow | Large caliber, large flow, high throughput capacity | Small caliber, low flow, not suitable for instantaneous large flow |
| Durability | Suitable for long-term large flow operation, robust structure | Prone to wear from water impurities, more moving parts |
7.3. Comparison with High-Technology Meters
Comparison with ultrasonic meters: Ultrasonic meters determine flow rate by measuring the time difference of ultrasonic pulses traveling in the water stream, representing a major modern smart metering technology.
| Comparison Metric | WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Meter (Mechanical) | Ultrasonic Meter |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher (involves precision electronic components) |
| Accuracy Stability | Requires periodic calibration (due to mechanical wear) | Long-term maintenance-free (no moving parts, accuracy stable) |
| External Power | No external power needed (purely mechanical or battery for communication) | Usually requires battery or external power supply |
| Straight Pipe Requirement | Requires 10D straight pipe (for flow stability) | Low or no requirement for straight pipe segments |
| Durability | Mechanical parts are pressure-resistant, strong environmental adaptability | Electronic components are sensitive to temperature and humidity |
7.4. Comprehensive Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Cost-effectiveness analysis: The WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter offers excellent cost-effectiveness in "large flow, high durability" applications. Its simple structure, low maintenance costs, strong water quality adaptability, and reliable mechanical durability, make its Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) highly competitive over a long service life.
The company Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. ensures that the WPH meter provides superior flow handling capacity and lower operating maintenance costs compared to other meter types, thus earning customer preference.
8. FAQ
8.1. What is the ideal installation position for the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter?
Answer: The ideal installation position for the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is horizontal, meaning the meter's main axis must be parallel to the ground, and the register (dial) should face upward. This is crucial for ensuring uniform axial loading on the spiral wing and guaranteeing metering accuracy.
For optimal precision, the meter installation must strictly adhere to straight pipe requirements: there should be a straight pipe segment of no less than 10D (where D is the nominal diameter) upstream of the meter and no less than 5D downstream, to eliminate flow vortices and disturbances and ensure smooth water flow into the measuring chamber.
8.2. How can I determine if the meter reading is accurate?
Answer: Determining the accuracy of a WPH meter reading primarily involves the following methods:
Flow Point Verification: When the meter is operating at Permanent Flow (Q3), compare its reading with a calibrated standard container or a secondary standard meter. According to ISO 4064, the meter error must be within the specified limits.
Visual Inspection: Check the meter for leaks, clarity of the dial, and the absence of debris jamming the spiral wing.
Professional Calibration: The most reliable method is to follow the statutory metering cycle and send the meter to an accredited metrology institution for re-verification or calibration.
The manufacturing quality assurance from Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. ensures the meter's ex-factory precision meets the highest standards. If users suspect reading inaccuracies, they should contact professional personnel for inspection and calibration.
8.3. What is the average lifespan of a WPH water meter?
Answer: The average lifespan of a WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is typically around 10 to 15 years, depending on multiple factors:
Manufacturing Quality: The high-quality materials and precision manufacturing from Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. effectively reduce mechanical wear, ensuring a longer product lifespan.
Water Quality: Cleaner water with fewer impurities results in a longer meter lifespan; high hardness or high sediment water quality accelerates internal component wear.
Operating Conditions: Long-term operation near Overload Flow (Q4) or frequent operation at flow boundaries can also shorten the meter's lifespan.
Under reasonable operating conditions and with regular maintenance, a high-quality WPH meter can operate reliably for many years.
8.4. How is remote meter reading achieved for WPH meters?
Answer: Remote meter reading (AMR/AMI) for the WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is achieved by integrating an electronic module onto the mechanical meter base. The main methods include:
Pulse Output: A pulse sensor is installed on the register, outputting an electrical pulse signal for every fixed volume of water that passes through (e.g., 1 cubic meter).
Electronic Communication Module: The pulse signals are converted into communication protocols such as M-Bus, RS485, or wireless LoRa, and uploaded to the management platform via a data logger.
The company Ningbo Water Cube Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. provides WPH meter movements with reserved or integrated remote reading interfaces, enabling the combination of reliable mechanical metering with the convenience of smart management.
8.5. Is a spiral wing water meter suitable for measuring sewage?
Answer: The WPH Horizontal Spiral Wing Water Meter is primarily designed for measuring clean cold or hot water. For sewage containing significant fibers, large suspended solids, or high corrosivity, a spiral wing meter is not the ideal choice.
This is because impurities in sewage can easily:
Entangle or jam the spiral wing, leading to measurement stoppage or severe inaccuracy.
Accelerate the wear of the bearings and spiral wing blades, drastically shortening the meter's lifespan.
However, for non-corrosive raw water or recirculating cooling water containing only small amounts of silt or slight turbidity, the WPH meter, with its robust horizontal structure and relatively straight flow path, offers stronger resistance to impurities and better durability than small residential meters.



 عربى
عربى